 Team leader: Capucine Trollet
Team leader: Capucine Trollet
Our team is working on the molecular and cellular actors involved in human muscle regeneration, in muscle ageing and in muscular dystrophies including oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy (OPMD) and Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD).
More precisely we are working on RNA metabolism, muscle regeneration, muscle stem cells, and fibrosis, with the final aim of developing innovative therapeutic approaches.
We have a strong expertise on human cellular models (this includes Myoline, the platform for immortalization that we have initiated) – and xenotransplantation (this includes several immunodeficient mouse models and grafting procedures).
Themes currently developed in parallel and in synergy
- Dissection of the molecular mechanisms relevant to OPMD and muscle ageing
- Dissection of cellular communication during muscle ageing, fibrosis and regeneration
- Development of therapeutic approaches.

Team members
Capucine Trollet (DR2 INSERM, team leader)
Nami Altin (IR)
Mona Bensalah (IR)
Maria Bergas Buades (PhD student)
Anne Bigot (CR AIM)
Dounia Bouragba (PhD student
Gillian S Butler-Browne (DR1 INSERM, Emeritus)
Rokiatou Diarra (L3 apprentice)
Valentine Hanique (IE)
Jean Lacau St Guily (PUPH, Emeritus)
Kamel Mamchaoui (IR AIM)
Barbara Moreira Crisol (postdoc)
Hadidja-Rose Mouigni (PhD student)
Vincent Mouly (DR1 CNRS, Emeritus)
Laura Muraine (IR)
Elisa Negroni (Sorbonne University Junior Professorship)
Jessica Ohana (Engineer)
Contacts
Collaboration: France-Brazil International Associated Laboratory
Another specific aspect of our team is the development of international collaborations. In addition to numerous collaborations established over many years, we have set up an International Associated Laboratory between INSERM and Sorbonne University for France and FIOCRUZ and the Federal University of Rio de Janeiro for Brazil.
 The IAL aims to synergise the expertise in muscle and neuromuscular diseases of French teams and the expertise in immunology and inflammation of the Brazilian teams.
The IAL aims to synergise the expertise in muscle and neuromuscular diseases of French teams and the expertise in immunology and inflammation of the Brazilian teams.
The IAL has already been renewed once, has resulted in 14 publications and a common patent, as well as the exchange of three long-term post-docs, 5 jointly supervised PhDs and many short term exchanges, including visiting professorships in both countries. A common training component (masters and / or doctoral program) is being developed and will involve innovative Biotherapies in the muscle environment.
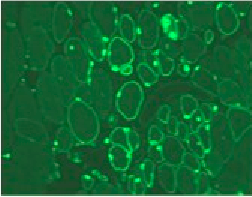
Figure legend: Human myoblasts in the damaged muscle of an immunodeficient mouse, identified by species-specific antibodies
Last publications
- Tissue-specific methylomic responses to a lifestyle intervention in older adults associate with metabolic and physiological health improvements. Sinke L, Beekman M, Raz Y, Gehrmann T, Moustakas I, Boulinguiez A, Lakenberg N, Suchiman E, Bogaards FA, Bizzarri D, van den Akker EB, Waldenberger M, Butler-Browne G, Trollet C, de Groot CPGM, Heijmans BT, Slagboom PE. Aging Cell. 2025 Apr;24(4):e14431. doi: 10.1111/acel.14431. Epub 2024 Dec 1. PMID: 39618079
- [Effects of physical exercise in muscular dystrophies]. Boulinguiez A, Bouragba D, Crisol B, Bigot A, Butler-Browne G, Trollet C. Med Sci (Paris). 2024 Nov;40 Hors série n° 1:17-21. doi: 10.1051/medsci/2024161. Epub 2024 Nov 18.
- The potential of proteomics for in-depth bioanalytical investigations of satellite cell function in applied myology. Dowling P, Trollet C, Muraine L, Negroni E, Swandulla D, Ohlendieck K. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2024 May-Jun;21(5-6):229-235. doi: 10.1080/14789450.2024.2356578. Epub 2024 May 20. PMID: 38753566 Free article. Review.
- How Can Proteomics Help to Elucidate the Pathophysiological Crosstalk in Muscular Dystrophy and Associated Multi-System Dysfunction? Dowling P, Trollet C, Negroni E, Swandulla D, Ohlendieck K. Proteomes. 2024 Jan 16;12(1):4. doi: 10.3390/proteomes12010004. PMID: 38250815
- SETDB1 modulates the TGFβ response in Duchenne muscular dystrophy myotubes. Granados A, Zamperoni M, Rapone R, Moulin M, Boyarchuk E, Bouyioukos C, Del Maestro L, Joliot V, Negroni E, Mohamed M, Piquet S, Bigot A, Le Grand F, Albini S, Ait-Si-Ali S. Sci Adv. 2024 May 3;10(18):eadj8042. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adj8042. Epub 2024 May 1. PMID: 38691608
- Different outcomes of endurance and resistance exercise in skeletal muscles of Oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy. Boulinguiez A, Dhiab J, Crisol B, Muraine L, Gaut L, Rouxel C, Flaire J, Mouigni HR, Lemaitre M, Giroux B, Audoux L, SaintPierre B, Ferry A, Mouly V, Butler-Browne G, Negroni E, Malerba A, Trollet C. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2024 Oct;15(5):1976-1988. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.13546. Epub 2024 Aug 7. PMID: 39113268
- [Nuclear aggregates in oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy]. Boulinguiez A, Roth F, Mouigni HR, Butler-Browne G, Mouly V, Trollet C. Med Sci (Paris). 2022 Dec;38 Hors série n° 1:13-16. doi: 10.1051/medsci/2022175. Epub 2023 Jan 16. PMID: 36649629
- Update on anti-fibrotic pharmacotherapies in skeletal muscle disease. Muraine L, Bensalah M, Butler-Browne G, Bigot A, Trollet C, Mouly V, Negroni E. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2023 Feb;68:102332. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2022.102332. Epub 2022 Dec 23. PMID: 36566666
- 3D human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived bioengineered skeletal muscles for tissue, disease and therapy modeling. Pinton L, Khedr M, Lionello VM, Sarcar S, Maffioletti SM, Dastidar S, Negroni E, Choi S, Khokhar N, Bigot A, Counsell JR, Bernardo AS, Zammit PS, Tedesco FS. Nat Protoc. 2023 Apr;18(4):1337-1376. doi: 10.1038/s41596-022-00790-8. Epub 2023 Feb 15. PMID: 36792780
- Our journey with François Gros. Butler-Browne G, Mouly V. C R Biol. 2023 Dec 19. doi: 10.5802/crbiol.140. Online ahead of print. PMID: 38113101
- T cell biology in neuromuscular disorders: a focus on Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Lemos JP, Tenório LPG, Mouly V, Butler-Browne G, Mendes-da-Cruz DA, Savino W, Smeriglio P. Front Immunol. 2023 Oct 18;14:1202834. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1202834. eCollection 2023. PMID: 37920473
- Myostatin in idiopathic inflammatory myopathies: Serum assessment and disease activity. Mahoudeau A, Anquetil C, Tawara N, Khademian H, Amelin D, Bolko L, Silvestro M, Cin JD, Tendrel B, Tardif V, Mariampillai K, Butler-Browne G, Benveniste O, Allenbach Y. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2023 Feb;49(1):e12849. doi: 10.1111/nan.12849. Epub 2022 Oct 7. PMID: 36168256
- HSPB8 frameshift mutant aggregates weaken chaperone-assisted selective autophagy in neuromyopathies. Tedesco B, Vendredy L, Adriaenssens E, Cozzi M, Asselbergh B, Crippa V, Cristofani R, Rusmini P, Ferrari V, Casarotto E, Chierichetti M, Mina F, Pramaggiore P, Galbiati M, Piccolella M, Baets J, Baeke F, De Rycke R, Mouly V, Laurenzi T, Eberini I, Vihola A, Udd B, Weiss L, Kimonis V, Timmerman V, Poletti A. Autophagy. 2023 Aug;19(8):2217-2239. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2023.2179780. Epub 2023 Feb 28. PMID: 36854646 Free PMC article.
- Caveolae and Bin1 form ring-shaped platforms for T-tubule initiation. Lemerle E, Lainé J, Benoist M, Moulay G, Bigot A, Labasse C, Madelaine A, Canette A, Aubin P, Vallat JM, Romero NB, Bitoun M, Mouly V, Marty I, Cadot B, Picas L, Vassilopoulos S. Elife. 2023 Apr 21;12:e84139. doi: 10.7554/eLife.84139. PMID: 37083699 Free PMC article.
- Prime editing strategies to mediate exon skipping in DMD gene. Happi Mbakam C, Roustant J, Rousseau J, Yameogo P, Lu Y, Bigot A, Mamchaoui K, Mouly V, Lamothe G, Tremblay JP. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 May 25;10:1128557. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1128557. eCollection 2023. PMID: 37305116 Free PMC article.
- Aberrant Adenosine Triphosphate Release and Impairment of P2Y2-Mediated Signaling in Sarcoglycanopathies. Benzi A, Baratto S, Astigiano C, Sturla L, Panicucci C, Mamchaoui K, Raffaghello L, Bruzzone S, Gazzerro E, Bruno C. Lab Invest. 2023 Mar;103(3):100037. doi: 10.1016/j.labinv.2022.100037. Epub 2023 Jan 10. PMID: 36925196
- High-capacity adenovector delivery of forced CRISPR-Cas9 heterodimers fosters precise chromosomal deletions in human cells. Tasca F, Brescia M, Liu J, Janssen JM, Mamchaoui K, Gonçalves MAFV. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2023 Feb 22;31:746-762. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2023.02.025. eCollection 2023 Mar 14. PMID: 36937620
- Tetraspanin CD82 Associates with Trafficking Vesicle in Muscle Cells and Binds to Dysferlin and Myoferlin. Fontelonga T, Hall AJ, Brown JL, Jung YL, Alexander MS, Dominov JA, Mouly V, Vieira N, Zatz M, Vainzof M, Gussoni E. Adv Biol (Weinh). 2023 Jul 12:e2300157. doi: 10.1002/adbi.202300157. Online ahead of print. PMID: 37434585
- Bioengineering a miniaturized in vitro 3D myotube contraction monitoring chip to model muscular dystrophies. Rose N, Estrada Chavez B, Sonam S, Nguyen T, Grenci G, Bigot A, Muchir A, Ladoux B, Cadot B, Le Grand F, Trichet L. Biomaterials. 2023 Feb;293:121935. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2022.121935. Epub 2022 Dec 13. PMID: 36584444
- Cellular and Genomic Features of Muscle Differentiation from Isogenic Fibroblasts and Myoblasts. Benarroch L, Madsen-Østerbye J, Abdelhalim M, Mamchaoui K, Ohana J, Bigot A, Mouly V, Bonne G, Bertrand AT, Collas P. Cells. 2023 Aug 3;12(15):1995. doi: 10.3390/cells12151995. PMID: 37566074 Free PMC article.
- Muscle Specific Promotors for Gene Therapy – A Comparative Study in Proliferating and Differentiated Cells. Dietz J, Jacobsen F, Zhuge H, Daya N, Bigot A, Zhang W, Ehrhardt A, Vorgerd M, Ehrke-Schulz E. J Neuromuscul Dis. 2023;10(4):575-592. doi: 10.3233/JND-221574. PMID: 37270809 Free PMC article.
- Targeting Duchenne muscular dystrophy by skipping DMD exon 45 with base editors. Gapinske M, Winter J, Swami D, Gapinske L, Woods WS, Shirguppe S, Miskalis A, Busza A, Joulani D, Kao CJ, Kostan K, Bigot A, Bashir R, Perez-Pinera P. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2023 Jul 27;33:572-586. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2023.07.029. eCollection 2023 Sep 12. PMID: 37637209 Free PMC article.
- Autosomal dominant in cis D4Z4 repeat array duplication alleles in facioscapulohumeral dystrophy. Lemmers RJLF, Butterfield R, van der Vliet PJ, de Bleecker JL, van der Pol L, Dunn DM, Erasmus CE, D’Hooghe M, Verhoeven K, Balog J, Bigot A, van Engelen B, Statland J, Bugiardini E, van der Stoep N, Evangelista T, Marini-Bettolo C, van den Bergh P, Tawil R, Voermans NC, Vissing J, Weiss RB, van der Maarel SM. Brain. 2023 Sep 13:awad312. doi: 10.1093/brain/awad312. Online ahead of print. PMID: 37703328
- Identification of a muscle-specific isoform of VMA21 as a potent actor in X-linked myopathy with excessive autophagy pathogenesis. Cocchiararo I, Cattaneo O, Rajendran J, Chabry F, Cornut M, Soldati H, Bigot A, Mamchaoui K, Gibertini S, Bouche A, Ham DJ, Laumonier T, Prola A, Castets P. Hum Mol Genet. 2023 Sep 26:ddad164. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddad164. Online ahead of print. PMID: 37756622
- CRISPR-Cas9 KO Cell Line Generation and Development of a Cell-Based Potency Assay for rAAV-FKRP Gene Therapy. Geoffroy M, Pili L, Buffa V, Caroff M, Bigot A, Gicquel E, Rouby G, Richard I, Fragnoud R. Cells. 2023 Oct 12;12(20):2444. doi: 10.3390/cells12202444. PMID: 37887288 Free PMC article.
- CRISPR-Cas9 editing of a TNPO3 mutation in a muscle cell model of limb-girdle muscular dystrophy type D2. Poyatos-García J, Blázquez-Bernal Á, Selva-Giménez M, Bargiela A, Espinosa-Espinosa J, Vázquez-Manrique RP, Bigot A, Artero R, Vilchez JJ. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2023 Jan 11;31:324-338. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2023.01.004. eCollection 2023 Mar 14. PMID: 36789274 Free PMC article.
- A homozygous loss of function variant in POPDC3: From invalidating exercise intolerance to a limb-girdle muscular dystrophy phenotype. De Ridder W, de Vries G, Van Schil K, Deconinck T, Mouly V, Straub V, Baets J. Neuromuscul Disord. 2023 May;33(5):432-439. doi: 10.1016/j.nmd.2023.04.003. Epub 2023 Apr.

